With our strong, sustained contribution in international research projects, often in a leading role, we help advancing the state of the art in Big Datacube technology, application, and standardization.
Current Projects

SkyFed:
Location-Transparent Earth/Sky Federation
"Data is the new gold", and this gold keeps pouring down on us from sky, as Earth Observation satellites deliver multi-Terabytes of spatio-temporal data daily. However, severe obstacles hinder us from optimal exploitation: transmission limits, processing limitations, incompatibilities, and several more.
SkyFed pushes the state of the art in Big Datacube Analytics available on edge devices, specifically: on nano satellites. To this end, the rasdaman datacube engine gets ported to a Raspberry Pi single-board computer which then gets deployed on a nano-satellite built from inexpensive off-the-shelf components and using common IT standards. This setup is used for demonstrating federated cloud/edge datacube processing connecting the satellite with existing multi-Petabyte Earth datacube services, including Copernicus archives and weather forecasts.
Thanks to the strict use of open standards, a wide range of 3rd party clients can readily tap into this integrated datacube space, allowing users and tools (like edge devices as consumers) to remain in the comfort zone of their well-known interfaces, despite the heterogeneity of the underlying data.
With its innovative edge intelligence, SkyFed opens the door for integrated data mashups spanning data centers, cloud, airborne and ship drones, and satellites in location-transparent federations enabling users to see a single, homogenized information space ready for zero-coding mix & match of Big Datacubes.
Runtime 2025/10 - 2027/09, EU EFRE Bremen overall funding support 748731€.
Project Partners





FAIRgeo: Fencing AI for Enhanced Reliability in Geo Services
FAIRgeo looks at AI on geo data, which is receiving high attention currently. However, literature that AI models are primarily reliable on their training data (e.g., 85%) and drastically unreliable outside it (e.g., 20%). The illustration shows a field fruit classification in the Netherlands, applying a model produced by Wageningen Research. It is clearly visible how the model hallucinates over water (bottom left), providing incorrect results.
We summarize the capability of a server to recognize invalid data/model combinations and react appropriately as "model fencing" to express that AI models during their inference get constrained to their individual application conditions ("comfort zone"). FAIRgeo attempts to structure the field and find decision criteria for selected situations.
Runtime 2025/03 - 2027/02, EU EFRE Bremen overall funding support 249922€.
Project Partners:
Constructor University, DE; rasdaman GmbH, DE




Past Projects

FAIRiCUBE: F.A.I.R. Information Cubes
The core objective of EU H2020 FAIRiCUBE is to enable players from beyond classic Earth Observation (EO) domains to provide, access, process, and share gridded data and algorithms in a FAIR and TRUSTable manner.
To reach this objective, we propose creating the FAIRiCUBE HUB, a crosscutting platform and framework for data ingestion, provision, analysis, processing, and dissemination, to unleash the potential of environmental, biodiversity and climate data through dedicated European data spaces. Within this project, TRL 7 will be attained, together with the necessary governance aspects to assure continued maintenance of the FAIRiCUBE HUB beyond the project lifespan.
Project Partners: Norwegian Institute for Air Research, NO (coordinator); Stichting Wageningen Research, NL; space4environment, LU; Constructor University, DE; 4sfera Innova SL, ES; EOX IT Services GmbH, AT; Epsilon Italia srl , IT; Naturhistorisches Museum Wien, AT; rasdaman GmbH (via subcontract)

|
This project has received funding from the Horizon Europe programme under grant agreement No 101059238 . |
AI-Cube
AI-Cube: Integrating Machine Learning with Datacubes
In the AI-Cube project datacube fusion and AI-based analytics will be integrated, demonstrated in several real-life application scenarios, and deployed on a federation of CODE-DE DIASs and further high-volume EO/geo data offerings.
Goal is to support scenarios like the following: User selects a topic (in the project: specific crop types, specific forest types, burnt forest areas). The system determines, through a combined analysis of various large-scale data sources, a list of regions showing the criterion selected. User gets this visualized directly or continues analysing, possibly combining with further data sources.
Project Partners: Jacobs University Bremen, Technische Universität Berlin (Prof. Dr. Begüm Demir)
| This project is co-funded by German BMWi (Federal Ministry of Economics). |
DynAWI
DynAWI: Dynamische Agrarwetterindikatoren zur Extremwetterprognose in der Landwirtschaft mit Methoden der künstlichen Intelligenz und Datacube-Technologie
In DynAWI verbinden wir Methoden der künstlichen Intelligenz und des Maschinellen Lernens mit Systemen zur Bereitstellung und Prozessierung von Geodaten, um aktuelle, räumlich und zeitlich hoch aufgelöster thematischer Karten von Agrarwetterindices für die Landwirtschaft zu erstellen. Die Agrarwetterindices werden mit kontinuierlichen Meßdaten aus dem Gelände validiert, um die Unsicherheiten der Indices zu bestimmen und darzustellen. Am Beispiel von Dürre/Trockenheit, Spätfrost und Bodenerosion durch Wasser werden an zahlreichen Standorten Agrarwetterindikatoren (AWI) identifiziert und Modelle für regionsspezifische raumzeitliche Prognosen von Extremwettersituationen entwickelt. Aufgrund der großen Datenmenge einbezogener Erdbeobachtungsdaten (insbesondere Sentinel-2, Witterungsdaten) und der Komplexität der Analysen nutzen wir die Datacube-Technologie, um diese "Big Data" in der Umsetzung von Prozessketten managen zu können. Wir streben an, die resultierenden Datenwürfel-Dienste in die GAIA-X-Umgebung zu integrieren. Die technischen Anforderungen hierfür werden innerhalb des deutschen GAIA-X Hubs (Agriculture, Geoinformation) abgestimmt.
DynAWI ist ein Verbundvorhaben von Julius Kühn-Institut, Universität Augsburg, rasdaman GmbH, Soilution GbR und AtmoScience GmbH und wird durch Mittel des Bundesministeriums für Ernährung und Landwirtschaft gefördert.

|
This project has been co-funded by German BMEL (Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture). |

Cube4All
Cube4All has established a commercial Earth data service leveraging the advantages of open standards based data-cube analytics. It makes complex EO tasks simple, keeping simple tasks simple; it unleashes EO analytics and fusion for non-EO / non-IT experts while increasing the productivity of experts. The resulting service stands out through
- genuine datacube services on several public Copernicus and further data offerings, including DIASs, CODE-DE and further large-scale data archives in a seamless manner;
- allows customers to either rent these services or rent their own preconfectioned datacube service (private or public-facing) on own data, or any combination;
- more user-friendliness, provably convenient for IT / EO experts and non-experts alike, from extraction to analytics without any programming;
- seamlessly integration of Copernicus and INSPIRE data;
- providing configurable access control for data customers want to offer;
- offers a particularly flexible, fair, and attractive billing model;
- APIs strictly based on the OGC/ISO/INSPIRE standards WCS, WCPS, WMS, and OAPI-Coverages;
This way, the developer of the rasdaman technology, rasdaman GmbH, plans to expand its business from software licensing into paid EO datacube services on public data offerings like DIASs. ESA Incubed+ enables this transformation of the company’s business model. Ultimately, the goal is to enable non-EO and non-IT users to utilize datacube services, as opposed to, e.g., own python or JavaScript programming.
Development of an appropriate business model and corresponding service setup on public data offerings is the core purpose of the Cube4All project.

|
This project is co-funded through ESA InCubed+. |
CENTURION
Copernicus is producing increasingly large data volumes that require specific Big Data technologies and Artificial Intelligence (AI) methods to analyse it and manage it. The adoption of Big Data technologies in the space industry represents a significant opportunity to innovate.
In addition, solving the big data management challenges of the integration, processing and analysis of Copernicus data with other distributed data sources from other industrial domains other than Space opens up new market avenues and strengthen European leadership in earth observation applications and technologies.
CENTURION develops, demonstrates, and operationalizes ground-breaking advances in Big Data and Artificial Intelligence. It gives consistent and easy access to combination of EO Analysis-Ready Data and AI analytics methods, making exploitation of Copernicus data easy for large groups of experts and non-expert users.

|
This project has received support by the European Commission under H2020 grant no 101004311. |
LandSupport: building Smart GeoSpatial Decision Support
The objective of EU H2020 LANDSUPPORT is the construction of a web-based smart geoSpatial Decision Support System (S-DSS), which shall provide a powerful set of tools devoted to (i) support sustainable agriculture/forestry, (ii) evaluate trade-off between land uses (including spatial planning) and (iii) contribute to implementation, impact and delivery of about 20 European land policies and also selected 2030 UN Sustainable Development Goals including climate change resilience goals and the key SDG 15.3 “achieving a land degradation-neutral world”. This objective is achieved by the integration of already existing databases (interoperability) at different scales with the development of high performance modelling engines simulating agriculture & forestry (e.g.crop growth), land degradation and environmental issues (e.g.fate of pollutants, ecosystem services). All the above, including their validation by remote sensed data, are be ensured by a technology at the state of art for the developing environment (i.e. COMPSs), high-performance computing and massive raster data management (rasdaman). LANDSUPPORT is applied at four geographic scales: EU; 3 Nations (Italy, Hungary, Austria); 2 European Regions in IT and HU; 3 pilot sites in AU, IT, HU; and 2 pilot sites in Tunisia and Malaysia. By doing that, LANDSUPPORT reconciles grand agriculture/environmental sustainability policy ambitions with operational reality such as the evaluation of "land use trade-offs" and "incentivizing real actions/behaviour/ investments"; all requiring activities at detailed spatial scale.

|
This project has been supported by the European Commission under H2020 project no 774234-2. |
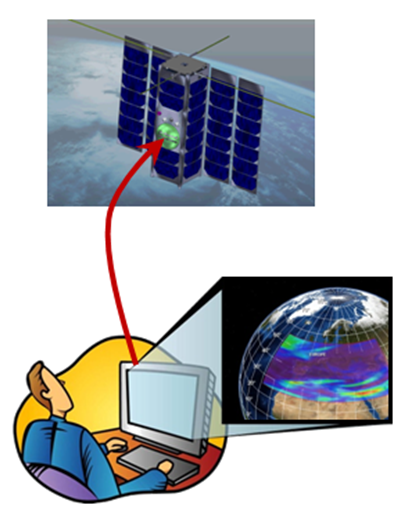

ORBiDANSe: Orbital Big Data Analytics Service
This project drives the "ship code to data" paradigm to the extreme: it makes a Cubesat an online Web data service for real time EO acquisition, processing, and retrieval, based on the ISO Array SQL standard under adoption. Images get acquired by the on-board camera and geo-referenced via GPS. Access is done via a high-level array query language allowing ad-hoc processing and filtering on spatio-temporal raster data, similar to what standard SQL accomplishes on tuple sets.
On board, such queries are evaluated by the rasdaman Big Array Data Analytics engine. Among others, it supports spatio-temporal queries, hence is truly multi-dimensional. The configuration can be updated/reconfigured in-flight, although emphasis is put on automatic optimization, including acquisition planning based on incoming queries. In a direct scenario, targeted subsetting/pocessing of imagery can be downlinked directly to the requesting client, effectively turning the satellite into an image database. In a federated scenario, a client may submit some complex decision support query to a data center; the rasdaman instance there finds out that data are missing and spawns a sub-request to the Cubesat; merges its locally computed results with the Cubesat response into the final result sent back to the user. As rasdaman is already cloud-parallelized, queries can be distributed automatically between ground and space instances.
Overall goal is to achieve a quantum leap in both EO service quality, data availability, and service integration.
This project has been supported by German BMBF (Ministry of Education and Research).
PARSEC
PARSEC aims to provide SMEs from the Earth Observation (EO) sector and key emerging industries (food, energy, environment) with access to capital, knowledge, market and technology services that allows them to forge new, cross-sectoral industrial value chains and realise significant, EO-enabled societal, economic and environmental benefits. PARSEC’s goals are pursued through (i) the introduction of an innovative selection and funding scheme, (ii) the provision of a portfolio of supporting services and (iii) the implementation of three large scale demonstrators (LSD), acting as enablers for the development of new EO-based products/services that bring key benefits to emerging industries. The foundations for PARSEC are provided by existing European assets; Copernicus the European flagship programme and its nascent DIAS (Data and Information Access Service), eoMALL, ESA TEP's and other linked programmes such as the European Open Science Cloud - linking industry and academia.
rasdaman being an accepted industry leader in datacube tools and standardization is contributing to several PARSEC work packages; in particular, the company is leading the PARSEC Big Data Toolbox development building datacubes on the Mundi DIAS, thereby acting as an enabling platform for SMEs to rapidly set up value-adding EO services and business models.

|
This project has been supported by the European Commission under H2020 project no 824478. |
EOSC-hub
EOSC-hub brings together multiple service providers to create the Hub: a single contact point for European researchers and innovators to discover, access, use and reuse a broad spectrum of resources for advanced data-driven research. For researchers, this means a broader access to services supporting their scientific discovery and collaboration across disciplinary and geographical boundaries. The project mobilises providers from the EGI Federation, EUDAT CDI, INDIGO-DataCloud and other major European research infrastructures to deliver a common catalogue of research data, services and software for research.
With rasdaman, we contribute the EOSChub EO Datacube component.

|
This project has been supported by the European Commission under H2020 project no 777536. |
CopHub.AC
The vision of the Horizon 2020 project CopHub.AC is to establish a long-term Copernicus hub to consolidate and sustain the Copernicus Academy as a knowledge and innovation platform. To fulfill this several nodes is created – like a new form of research briefs, knowledge landscape, outreach and sustainability. It focuses and link ongoing R&D activities in Copernicus-relevant academic fields and sustain the innovation process from academia to business on a high scientific and technical level. We have a clear commitment to a full thematic and geographic coverage for a Europe-wide boost in demand-driven uptake of space technology and geospatial information.

|
This project has been supported by the European Commission under H2020 project no 821952. |
[ project flyer ]
BigDataCube: Flexible, Scalable User Services on Massive Spatio-Temporal Earth Observation Data
The BigDataCube project aims at advancing the innovative datacube paradigm – i.e., analysis-ready spatio-temporal raster data – from the level of a scientific prototype to pre-commercial Earth Observation (EO) services. To this end, the Germany-based, worldwide leading datacube technology (in database lingo: “Array Database”) rasdaman is installed on CODE-DE as well as in a commercial cloud environment to exemplarily offer analytics services prototypically.
Complementing the Hadoop service already available on CODE-DE rasdaman offers important additional functionality, in particular a paradigm of "any query, any time, on any size", strictly based on open geo standards and federated with other data centers. On this platform novel, specialized services can be established by third parties in a fast, flexible, and scalable manner.
To this end, several features crucial for operational services need to be tested and/or implemented, such as securing access (in particular in a federation context), optimal operation in a cloud configuration like CODE-DE, support for radar data, and further items to be determined in the initial requirements analysis phase. The result is the prototype of a federation of rasdaman installations on CODE-DE, CloudEO, as well as the (external) EarthServer federation; further, best practices on the use of array databases in operational environments are established. This paves the way for individual value-adding services by third parties.
This project has been supported by German BMWi (Ministry of Economy and Energy).

[ project flyer ]
BigPicture: Big Data in Agriculture
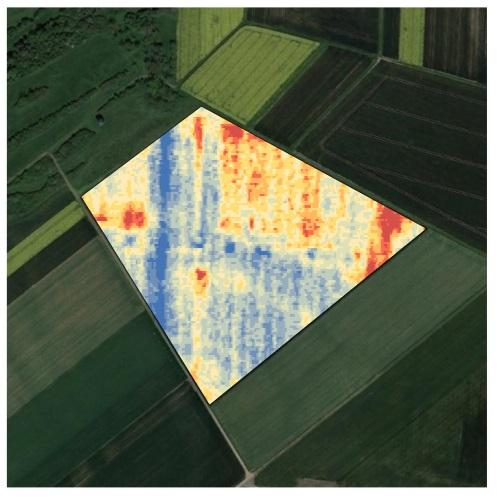
This project has addressed diagnosis in the farm field through Big-Data-based determination of causes for satellite image derived and site-specific variations.
BigPicture has established services to help farmers to optimize returns and to protect the environment through innovative Big Data technology. By interpreting satellite captured variations in farm fields through Big Data technologies targeted measures, such as fertilizer placement, application of plant protection products, or choice of species to grow, can be derived. Manifold information is combined in such analyses, including satellite imagery, weather data, as well as the farmers’ experience. This way, the processing chain from satellite-based symptoms captured in the field over diagnosis up to therapy recommendation can be automated entirely.
Internationally recognized experts have teamed up: Spatial Business Integration GmbH is a specialist in satellite-image based information products for agriculture, rasdaman GmbH is an expert in Big Data services. By combining the complementary know-how of both partners BigPicture has established large-scale automated analysis offering individual insights and support for agricultural production in Germany.
This project has been supported by German BMEL (Ministry of Food and Agriculture).

DIN-CONNECT: Establishing the Next-Generation ISO Coverage Standard
German standardization body, DIN, has tasked rasdaman GmbH with establishing the next-generation high-level coverage standard, ISO 19123-1 Abstract Coverage Model. Based on the fact that the company already has established the OGC Coverage Implementation Schema, which meantime is adopted by ISO as 19123-2, DIN relies on the unmatched experience of rasdaman GmbH when it comes to coverages and datacubes.
This project has been supported by German DIN.
EVO-ODAS: Evolution of EO Online Data Access Services
The technology project "Evolution of EO Online Data Access Services" analyses relevant scenarios and technologies for data publication and access, identifies potential for improvements of standards and their implementations, prototypes and evaluates selected improvements and proposes standard extensions for future releases.
The consultant rasdaman GmbH supports the consortium in the assessment of standards and the specification and demonstration of standard evolutions. rasdaman GmbH is a key contributor to a wide scope of geospatial data access standards within OGC and raster database access standards within ISO. It also provides a spatio-temporal Big Datacube solution with the scalable open source array engine rasdaman.
This project is funded by ESA.

[ project flyer ]
Earthserver-2: Agile Analytics on Big Data Cubes
As a followup to the extremely successful EarthServer, the intercontinental EarthServer initiative, funded by EU H2020, makes Agile Analytics on Big Earth Data Cubes of sensor, image, simulation, and statistics data a commodity for non-experts and experts alike.
Large-scale data centers are setting up water, air, weather, and planetary services on 3D and 4D Petabyte-size data cubes with user-tailored clients for both visual and textual queries for ad-hoc mix&match. Being in its second phase, EarthServer maintains and extends the lead in Big Earth Data services established in the highly successful phase 1. Being already supported by ESA, rasdaman is being established as an enabling building block for COPERNICUS / Sentinel.
rasdaman GmbH provides its enabling technology as the EarthServer platform, together with support for the data centers. The rasdaman technology is advanced in both scalability and functionality. Further, it contributes to standardization and leads exploitation work.
This project has been supported by the European Commission / EINFRA under H2020.

VISEO-FUSION: Video / Image / Sensor / EO - FUSION
ViseoFusion has designed, built and tested a multi-stream geospatial data platform that supports decision-making for operational agencies and critical infrastructure operators. Earth Observation imagery, in-situ datasets and existing web services are integrated, analyzed and visualized in order to provide the end-user with actionable information in either review or near real-time mode
rasdaman GmbH is providing its technology as a backend and information turnpike for various types of high-volume raster data.
Publicamundi: Scalable Reusable Open Geospatial Data
EU FP7 PublicaMundi is delivering methodologies, technologies and software components to leverage geospatial data as first-class citizens in the CKAN open data catalogue by combining reusable software components and tools enabling scalable, responsive, and multimodal value added applications on open geospatial data. Software components providing reusable, scalable, multi-lingual, and cost-efficient processing and analysis services for open geospatial data are being established, leveraging both vector and high-volume raster data.
rasdaman GmbH contributes its scalable raster engine, rasdaman, for integration with the widely used CKAN catalogue tool. This way, CKAN gets enabled with large-scale spatio-temporal raster data handling.

[ project flyer ]
EarthServer: open, flexible, scalable, and user-friendly access to spatio-temporal Earth science data
EarthServer has established services and technology for open, flexible, scalable, and user-friendly access to spatio-temporal Earth science data. Accessing such data ranges from simple navigation over extraction, download, filtering, and processing up to complex analytics. This is accomplished through versatile ad-hoc analytics suitable for extreme-size multi-dimensional Earth Science data, based on and extending leading-edge Array Database technology.
EarthServer combines both, thereby achieving tight data/metadata integration. Further, the rasdaman Array Database System is extended with further spatiotemporal coverage data types. On server side, highly effective optimizations -- such as parallel and distributed query processing -- ensure scalability to Exabyte volumes.
Several Lighthouse Applications, spanning all Earth sciences, have been established with up to 132 TB databases covering: atmosphere (climate modelling), hydrosphere (oceanography), lithosphere (geology), and cryosphere (snow and ice mapping); in addition, a air-borne science (drone) imagery database has been set up and a Planetary science use case with surface and subsurface data on Mars.
The main innovations of EarthServer are:
- Substantial simplification of use of any-size, any-dimension Big Earth Data, through flexible, scalable, integrated, standards-based access interfaces;
- Integrating data and metadata in Big Earth Data queries,
- Uniform access across space and time, enabling large image and weather timeseries;
- Web service support for across all OGC coverage types: multi-dimensional grids, point clouds, and meshes;
- Transparent queries across heterogeneous file archives and databases;
- Paving the way for Petabyte Copernicus and climate services through parallel and distributed processing of queries.
- Strict reliance on the open OGC standards for Big Earth Data access, Web Coverage Service (WCS) and Web Coverage Processing Service (WCPS), including advancing these standards themselves.
Nucleus is the pre-existing rasdaman system which has coined a new research field, Array Databases. During EarthServer, rasdaman has strengthened its position as the world‟s leading Array Database over recent competitors such as SciDB. This substantial technological advance has resulted in a series of awards for Jacobs Uni and rasdaman GmbH, such as winner of the Big Data challenge in the Copernicus Masters competition 2014.
A wide range of outreach activities has accompanied technology development and service de- ployment. Trainings, best practices, and auxiliary software tools have been provided at events and on the Web. A multitude of communication channels have been used to position the EarthServer technology worldwide (such as GEO Plenaries, Copernicus workshops, cli- mate data workshops, standardization meetings). A particular highlight is a 1h TV documentary titled “Big Earth Data – the digitized planet” (Fig. 3) done by Jacobs and rasdaman GmbH one in collaboration with German ZDF and ARTE, to be broadcast soon after the project. While focusing on Earth sciences, this project transcends Earth and Planetary data; rather, Array Databases comprise horizontal platform technology equally game-changing Life sciences, but also industry (such as oil and gas exploration) and eGovernment. In the latter context, during EarthServer INSPIRE has agree to base its Download Services for coverages on the OGC Web Coverage Service (WCS); work commenced in October 2014. To foster such uptake, industry and authorities have been involved in EarthServer.
TeraPro
In TeraPro, a flexible, powerful image processing tool, proStack, has been coupled with a scalable array database backend, rasdaman.






