SAR for Crop Mapping
Revealing the potential of dense temporal information provided by Sentinel-1
Croplands are characterized by strong temporal dynamics where the crop type on ground can be identified during a certain time period between seeding and harvesting. Hence, it is critical to have continuous temporal coverage over the individual growth periods. SAR is able to penetrate clouds and therefore delivers information independent of cloud coverage or daylight.
Researchers at the TU Darmstadt use these characteristics to explore the possibilities of satellite carried SAR systems to provide large-scaled crop type identification. Sentinel-1 dual-polarized images from an entire year were used for the analysis, amounting in 16 TB of data. Only one local training data set was used for the whole mapped area. The specifically developed image analysis procedures were implemented in Python and R. The entire process, starting with the download until the final map, was implemented fully automated.
Germany’s main crop types of 2018, including grasslands, were mapped. An update of the map is planned for 2019, which will contain more land cover and crop types. The land cover classification will also be implemented for further European countries and worldwide. The effect of radar shadow is aimed at being reduced as well.
The centerpiece of the processing environment is the rasdaman database which allows for fast and flexible management and accessibility of the data. For large multi-temporal data stacks, this database enormously increases the data mining potentials.
Detailed results can be found at www.coramaps.com.
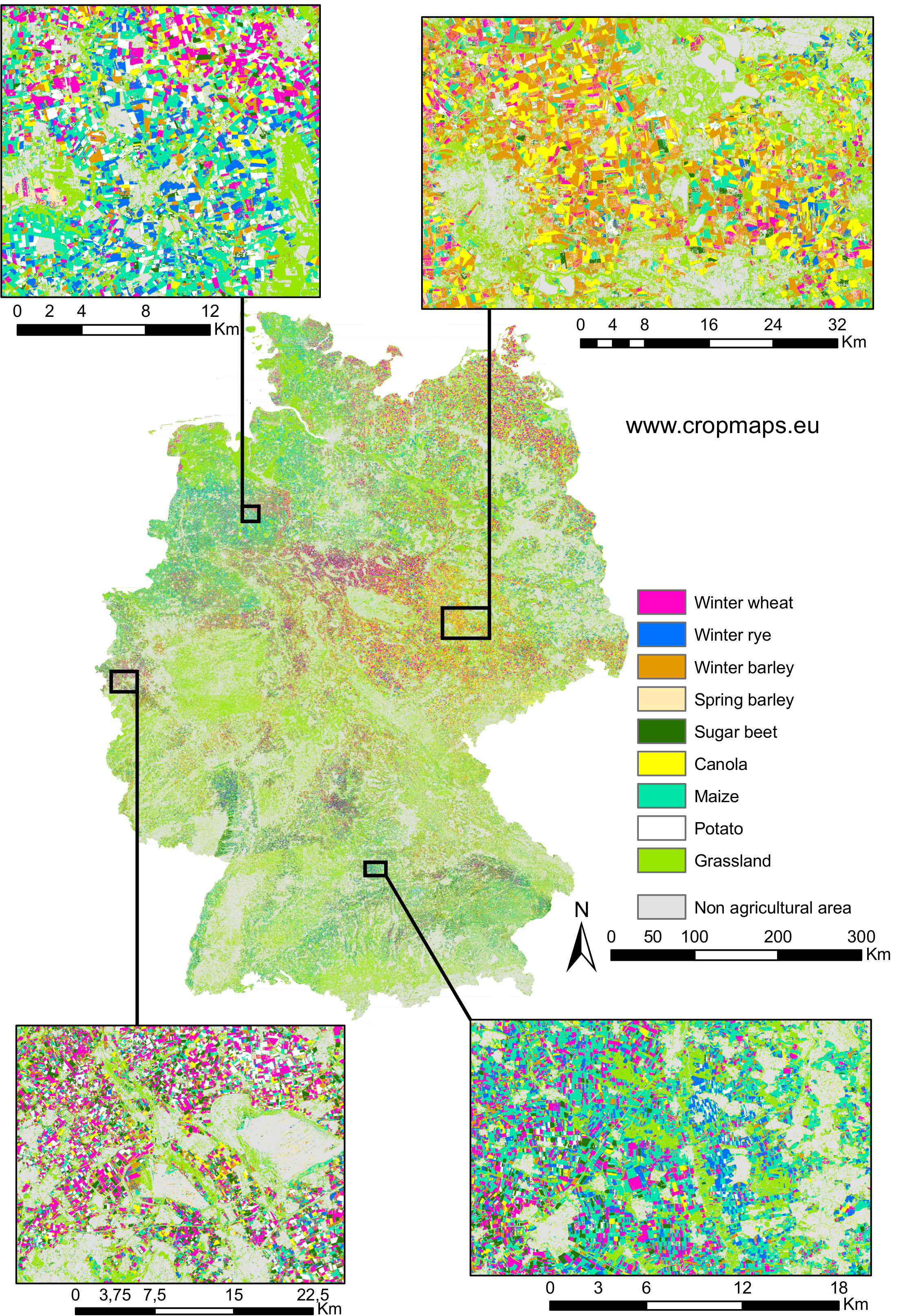
SAR-based crop yield classification by CORAmaps |
Contact: